


RGA Project Part 1
Project Description
Dining away from home is an extremely common experience in this age of convenience and many people make the decision to eat at a restaurant when they are already out in the community. These decisions are made more difficult when people are in an unfamiliar environment or surroundings. These people are in what we define as a mobile environment, in transit and away from their home, office, and any personally established location. They are in a unique situation in terms of dining in a restaurant because there is currently not a well-designed system available to find a restaurant while in a mobile environment. We seek to develop this well-designed system on a personal digitized assistant (PDA). More specifically we seek to support the tasks of finding a restaurant in terms of gaining information based on certain criteria, selecting a restaurant based on this information, establishing the directions to this restaurant from the present mobile location, and actually physically finding the restaurant. These tasks will be described in more detail in a later section. This system will be aimed at a user population which is of a variety of ages, but which is familiar with computer and PDA applications. PDAs were chosen for their extremely mobile and compact design. They are an emerging technology that is becoming more prevalent in society as a whole.
User Profile
In order to improve the userís ability to find restaurants in mobile situations, it is necessary to understand who users of this system will be. The users of the system include those individuals who attempt to find restaurants in a mobile environment. More specifically, the users are assumed to have reading skills, vision ability, and motor skills. Additionally, users of the system will be experienced and proficient in the use of PDA equipment, and thus, will be able to utilize the various features of a PDA with ease. The users are assumed to be either college students or business professionals. This distinction is made because these individuals most commonly own and frequently carry and operate PDA systems, according to results obtained from questionnaires and interviews.
Task Analysis
We have specified the users of the system and now it is important to designate the tasks that these users perform. In general, these tasks are associated with the overarching task of finding a restaurant. From an administered questionnaire, user interviews, and a focus group we found several tasks necessary to find a restaurant. These tasks include the following:
∑ Finding the restaurant
∑ Specifying criteria to base a search upon
∑ Search using these criteria for a restaurant
∑ Select the restaurant from the choices listed
∑ Making reservations (if applicable)
∑ Finding directions to the restaurant from the current location
∑ Traveling to restaurant
If a user is unfamiliar with an area and restaurants in that area, all of these tasks (except making reservations) will most likely be performed. However, if the user has some familiarity with the area, it may not be necessary for them to perform tasks such as specifying and searching by criteria since they may select a restaurant by name that they are already familiar with.
Task Environment
It is important to understand the environment in which the task must be performed to understand the problems and benefits of this environment in terms of the user performing the task. The system must be designed not only for the user and the tasks, but also considering the task environment. Thus, we will now discuss the various environments in which the task could be completed. All of these environments are assumed to involve finding a restaurant in a mobile environment, as this environment is inherent to the nature of the problem. It is also assumed that this mobile environment is in a relatively large city, since the use of many of the current systems is only functional in large cities and finding a restaurant in a small town involves different methodologies and tasks.
∑ The Vehicle- The User could attempt to complete the tasks while in a vehicle. In this environment there are several situations to consider.
∑ Driver as User, while operating vehicle- The first situation involves the user being the driver of the vehicle. In this case, the user not only has to accomplish the task of finding a restaurant, but he or she must also accomplish the task of driving the vehicle. Completing the task while driving makes it necessary to note issues such as divided attention and limitations on mental capabilities based on different forms of visual stimulation, from both the road and the restaurant searching stimulus. The driver as user will have to complete all tasks associated with finding a restaurant while also performing driving tasks such as obeying traffic signals, avoiding other traffic, and remaining on the appropriate course. Also, there are limitations on motor capabilities, since it is advisable to drive with at least one hand on the steering wheel. Additionally, the task of finding a restaurant can be performed in both familiar and unfamiliar locations. There are additional demands associated with an unfamiliar location for the driver and in this case the user. They are forced to perform tasks associated with driving with less automaticity, and as a result they are required to focus more attention on driving.
∑ Driver as User while vehicle is not in motion or Passenger as User- The driver could also be the user, but could engage in the task of finding a restaurant while not driving, that is, while the vehicle is stopped or parked. A passenger of the vehicle could also be performing the tasks associated with finding a restaurant. Regardless, the userís attention and mental focus will still be divided. The user will focus on surroundings, location, potentially conversing with others in the vehicle, and changing music or climate control. Thus, while there would be less mental demand placed on the user in this situation, it is nonetheless important to consider that the task will most likely be performed in a multi-task environment.
∑ Other Mobile Areas- The tasks could also be performed in such environments as city sidewalks while walking or standing. In these mobile environments the demands on the user would be similar to those faced by vehicle passengers as users, as long as no other tasks are being performed which require large amounts of attention and mental resources. Tasks associated with finding a restaurant could be performed while the user is familiar with his or her surroundings and location, in which case the task would be more automated and the user would be more likely to be familiar with available restaurants. However, the tasks could also be performed in an unfamiliar location, a situation in which the user would require more outside information, since they would be less familiar with restaurants in the area. In addition, they would have to devote more mental resources to the task of navigating their environment, which could limit attention available for the task of finding a restaurant. It could also affect performance on this restaurant search task.
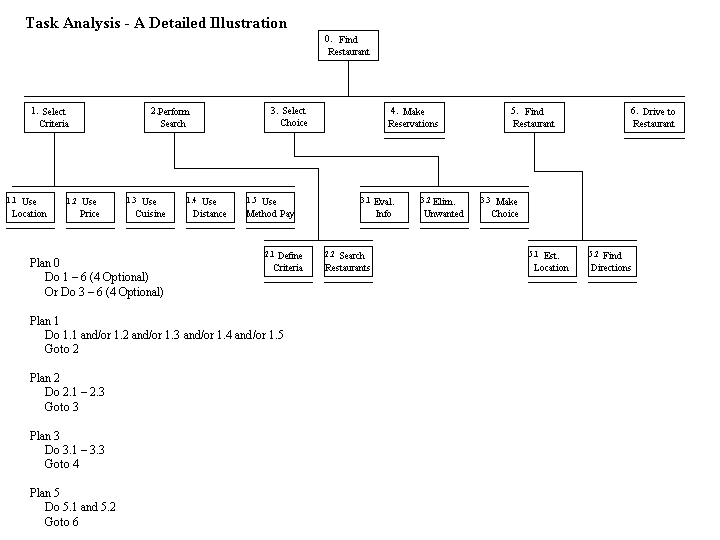
The task that is laid out in the task analysis is that of finding a restaurant while in a mobile environment. All other tasks involved in dining at a restaurant are not relevant to this analysis. With that in mind we would like to elaborate on each one of the points in the task analysis above.
1. Select Criteria: Selecting the criteria to search by is a crucial first step in finding a restaurant. Selecting the criteria to search by involves deciding whether or not to search using location, price, cuisine, distance, or method of pay. We make a distinction between selecting the criteria and defining the criteria
1.1 Use Location: Deciding to search for the restaurants in a given city using the location of the restaurant relative to the users current location
1.2 Use Price: Deciding to search for the restaurants in a given city using a given price range will be later defined by the user
1.3 Use Cuisine: Deciding to search for the restaurants in a given city sorting by the cuisine that is offered by the restaurants
1.4 Use Distance: Desiring to look for restaurants that are within a given distance from the users current location
1.5 Use method of pay: Some users may need to find out how they will be able to pay to help their decisions. That method of payment could be credit card, cash or check.
2. Perform Search: After the user decides which criteria they will use to search they must now physically perform the search in some manner. The user may use the five criteria that are listed above. We identified these five subtask in the task because they were the most common tasks mentioned by users. However, other criteria were identified as well. These include:
∑ Wait times
∑ Outdoor/Indoor dining
∑ Specific Menu Items
∑ Scores on Restaurant Reviews
∑ Atmosphere
∑ Presence of a Bar
21 Define Criteria Values: The act of choosing the value this wish to search by
2.2 Search Restaurants: The user actively searches for the restaurant or restaurants that meet or exceed the criteria they laid out in the previous steps
3. Select Choice: In this step the user must make a decision about the restaurants that the search has returned. They will be presented in list form with the description of the restaurant available to the user to aid in the decision if the user is unfamiliar with the given restaurant
3.1 Evaluate Information: The user must evaluate the results of their search into some form of hierarchy that will aid in the decision making process
3.2 Remove unwanted information: The user must eliminate items they know immediately they do not wish to consider or information that was given in error. Information given in error could exist among a list of valid information but was simply not what the user had in mind.
3.3 Make Choice: The user weighs the options of the results of the search and makes a decision on which restaurant to choose.
4. Make reservations: This step is optional for several reasons. One of these reasons could be reservations might not be appropriate at certain restaurants. Also, for one reason or another, the restaurant may not wish to allow reservations to be made over the internet or wireless technology due to a fear that the user might not actually show up.
5. Find restaurant: Finding directions to the restaurant that has been chosen using the new restaurant finder system
5.1 Establish Location: The user should figure out where they are currently so they can discern driving directions from the users location to the restaurant.
5.2 Find Directions: The user would be presented with two forms of directions to the chosen restaurant. The directions would either be in a visual map format or a text-based format.
6. Travel to Restaurant. This involves the user actually following the directions properly to ultimately arrive at the restaurant.
System Description
It is important to understand the current systems for accomplishing the task as well as the problems and benefits of these systems so that the design of a new system can incorporate the benefits and avoid the problems of the current systems. There are currently a variety of systems in use to accomplish the goal of finding a restaurant in a mobile environment. Each of these systems has various advantages, but all are seriously flawed on some level. Each system will be considered in turn.
∑ Advertisements- These include but are not limited to billboards, newspaper ads, and word of mouth. The advantages of advertisements are that they require little mental resources from the user, since the information regarding the restaurants is directly presented to them and no search is required. However, there are numerous disadvantages. They may not provide all the information the user wants. If this is the only method used, there is no way to acquire the additional desired information. Additionally, since advertisements are only placed in select locations, the user is not presented with all restaurant options.
∑ Calling Restaurants- This system includes directly phoning restaurants for information. The advantages include human-human interaction that results in the ability to ask for any information the user desires. This information may be more reliable as it comes directly from the source. There are several disadvantages associated with this system. It does not allow users to consider restaurants in a parallel manner. Instead they must be called individually, which is time consuming. It also limits restaurant choices to those with phone numbers readily available. Additionally, the user may not be provided with accurate directions to the restaurant. It also assumes users have access to a cellular phone or a payphone to complete the call.
∑ Internet search engine- This system allows the user to search for restaurants using web interfaces such as AccessAtlanta and Yahoo Restaurant Search. This system has several advantages including that it allows the user to search by several criteria. It provides information such as cuisine type, location and directions. It also allows the user to access reviews of the restaurants. Additionally, in a mobile situation it requires wireless Internet capabilities and is dependent upon the speed of these capabilities. The search engines are multi-layered websites, which often results in slow access and decreased ease of use. There are limitations of the breadth of information offered as well. For instance, they only show cuisine type and not menu options.
∑ Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) based search programs- There is a multitude of programs for PDA systems, which allow users to find a restaurant in a mobile environment. We performed a rather extensive evaluation of these systems since they are most closely related in terms of features and functionality to the system that we seek to create. Based on searching relevant literature we identified several of these programs, including Vindigo, Zagat, Avantgo, JunglePort, Cyberwaiter 1.1, and Food and Drink. We examined many of these available mobile systems. We chose to focus user testing on Vindigo, which in our opinion is the most advanced of these systems and provides the most similar functionality to what we wish to provide in a new system. Vindigo is a program developed for the PalmOS that provides the user with a list of restaurants and reviews of these places. It also provides text and map based directions to the destination. It can be used wirelessly if the device contains such features and it can use a GPS device to locate its current position.
Advantages:
∑ Provides an extensive list of restaurants for many major cities
∑ Allows you to load the information into your Palm ahead of time so that there is no delay in the retrieval of the information requested.
∑ Has a wireless sync option to request additional information on the go.
∑ Can interface with a GPS receiver to locate the personís present position.
∑ Allows user to search by name or cuisine type, and provide the closest restaurants to the current location.
∑ Provides a limited list of reviews based on the information source.
∑ Can provide text-based directions to the destination.
Disadvantages:
∑ Has an ad based system of revenue whereby you receive the occasional ad as the user of the device
∑ You must remember to download the data for whatever cities you plan to visit because most handheld devices do not contain adequate memory to store every possible city
∑ Does not allow the user to determine the location without a GPS, most wireless network options can provide the user with a general location.
∑ Not a seamless method of retrieving new information. To update the database you need to either sync with a computer or do it using wireless. This step should be transparent so that the user needs to know nothing about how it is done.
∑ Does not allow the user to perform advanced searching, such as multiple cuisines at once or by providing a price ceiling.
∑ Does not provide a way to view a partial or complete selection of menu items, or search based on this.
∑ Does not provide a consistent selection of information, information depends on the source from which it was gathered
∑ Does not provide an easy way to make reservations with the restaurant besides calling them up.
∑ Does not provide an easier to understand map (visual) based direction system, the one it provides is almost not usable.
Usability Criteria
There are a myriad of usability criteria that a designer should keep in mind when designing a system. These usability criteria serve as guidelines for the designer in making the overall system user-friendly and more efficient for the user. For our new system, we would like to focus our attention on, but not limit ourselves to, three specific usability criteria. The chosen criteria for this system are familiarity, customizability, and recoverability.
Familiarity: Familiarity refers to how past information and past experiences of the user with similar systems can be applied to the operation of a new system. This particular criterion goes to the learnability of a system. The new system and interface will be familiar to the user that is already familiar with the operation of various existing Internet search pages. We want our system to resemble these existing pages in so much as they have forms and fields for the user to make criteria distinctions. Also, it would be easy for the user to find items on the menu that is brought up by their search if that menu resembles the menu they would receive at the restaurant itself. In other words, appetizers first, followed by entrees, beverages and deserts. Following the users mental model of a menu system would aid in the learnability of the system.
Customizability: Customizability of the system refers to the ability of the user to tailor the system to their specific needs and desires. Our system will be able to search by different criteria. The user will specify these criteria and the user may omit or include any criteria they wish to search by. The system will be able to prioritize the criteria that the user has used in the past. The system will also be able to prioritize the results and information for the user.
Recoverability: Recoverability of a system refers to that systems ability to correct itself or allow the user to correct the system in the event of an error being made during operation. This is a very important usability criterion for any system. Recovering from errors in this system will involve the user being able to do one of two things. First the user will be able to start a completely new search in the event of an error. Second, the user will be able to go back to the form the previously used so they can merely change the one error in their search without having to completely start the search over with a blank form.
Reflections on Requirements Gathering
To assess the problem, including the users, tasks performed, current systems and usability criteria it was necessary to gather information relevant to the problem. Several methodologies were utilized to collect this information, including a user questionnaire and user interviews, a focus group of potential users, research of relevant literature, and observation of users performing the task using current systems.
User Questionnaire-
An open-ended questionnaire was administered to approximately 15 individuals of a variety of age ranges and backgrounds. This questionnaire identified the user profile for our proposed system, identified the current systems used, the benefits and problems of these systems, and established criteria upon which users most often base their restaurant selections. The questionnaire contained questions asking individuals what current systems they use and focused on systems that we had previously established, asking more explicit questions about these systems, specifically Internet based search engines for restaurants. The questionnaire was open-ended because we wanted potential users to provide as much information as possible about the task and we hoped to avoid limiting the individuals to certain systems or concepts.
The questions on this questionnaire and were as follows:
How do you get information about restaurants where you might be interested in eating?
How do you determine where you will eat when you are already away from home?
What criteria do you base your search on?
(Cost, cuisine, location, payment types accepted, parking, valet, etc)
Would it be helpful to have easy access to information about restaurants while away from home?
How do you search for restaurants when you are not in your hometown?
Do you often look up restaurants you have already been to for their phone number or address?
Do you call restaurants for information?
If so, what kinds of questions do you ask?
Do you usually get satisfactory answers?
What are the problems that you have encountered with any of these methods for finding a restaurant (indicate method and problem)?
How often do you get to a restaurant only to find that the line is longer than you are willing to wait?
Do you use Internet-based search pages to find information about restaurants?
If so...
a. How often do you use Internet-based restaurant search pages?
b. What criteria do you base your search on?
(Cost, cuisine, location, payment types accepted, parking, valet, etc)
c. Is a grouping of similar restaurants useful?
-By which criteria would you prefer to group the restaurants?
d. Do you trust the information that you find on the Internet about restaurants?
e. Do you have a preferred Website for searching for restaurant information?
f. What features set this site apart?
g. Are there features that are not there that you wish you could have?
h. Would being able to make reservations (when appropriate) be useful?
Do you own or have access to a PDA (Personal Digital Assistant)?
If so...
a. What do you use your PDA for?
b. Are you skilled at using your PDA and writing to it with the stylus
c. Do you access the Internet from your PDA?
d. How often do you carry your PDA?
User Focus Group-
After administering the general open-ended questionnaire, a focus group was conducted with several potential users who met the requirements of our specified user profile. This focus group expressed interest in acquiring a new system for completing the task of finding a restaurant while mobile, especially a new system on a palm device. The discussion in this focus group provided information concerning problems with current systems and methods through which users perform the task of finding a restaurant. For example, users indicated that often not all needed information is available on one system for completing the task. Even after searching based on certain criteria these potential users indicated that they often have to call the restaurant to obtain all information. Thus, they have to use two systems, wasting time and creating frustration, especially in a mobile situation.
Relevant Literature Review-
To gain more understanding of current systems in operation a literature review was performed. This literature review sought to find all relevant systems and to ascertain their effectiveness through critical analysis and reviews. The following web sites were viewed:
∑ To understand the internet search engine systems for finding a restaurant Access Atlanta (www.accessatlanta.com) and Yahoo Restaurants (restaurants.yahoo.com) were thoroughly inspected.
∑ To discover various applications and programs available for completing the task of finding a restaurant on PDAs various web sites were visited. These include Zagat (www.zagat.com), Avantgo (www.avantgo.com), JunglePort (www.jungleport.com), Cyberwaiter 1.1 (pda.rcp.net.pe/palm/preview/73852.html).
Usability Testing-
The userís opinion of the software available to find a restaurant on a PDA was obtained by conducting usability testing. We downloaded two of the current systems that are available on the Palm operating system and asked someone to act as a user and attempt to find a restaurant. The users actions were observed in order to determine features he spent more time on or features that gave the user difficulty. After the testing, we interviewed the user to obtain their objective opinion on how the system operated in its intended task.
Link to this Page
